File Allocation Methods
Contiguous Allocation
Each file is allocated a contiguous set of blocks.
graph TD
subgraph Filestore
eeny
meeny
miny
mo
end
Location of information consists simply of:
- Start Block
- Number of blocks.
Advantages
- Fast for both sequential and direct access.
Problems
- Fragmentation
- May need regular compaction.
- Number of blocks to allocate.
- File growth.
Linked Allocation
Each block contains a pointer to the next.
graph LR
subgraph Filestore
eeny1 --> eeny2
eeny2 --> eeny3
miny1 --> miny2
end
These blocks could be anywhere on the disk.
Could be improved by allocating blocks in clusters but this worsens internal fragmentation.
Advantages
- Easy to grow/shrink files.
- No Fragmentation.
Problems
- Blocks are widely dispersed.
- Sequential access less efficient.
- Direct access even worse.
- Requires $n$ reads to get to block $n$ (following the chain.
- Danger of pointer corruption.
File Allocation Table
Block allocations are held in a table located at the start of the partition.
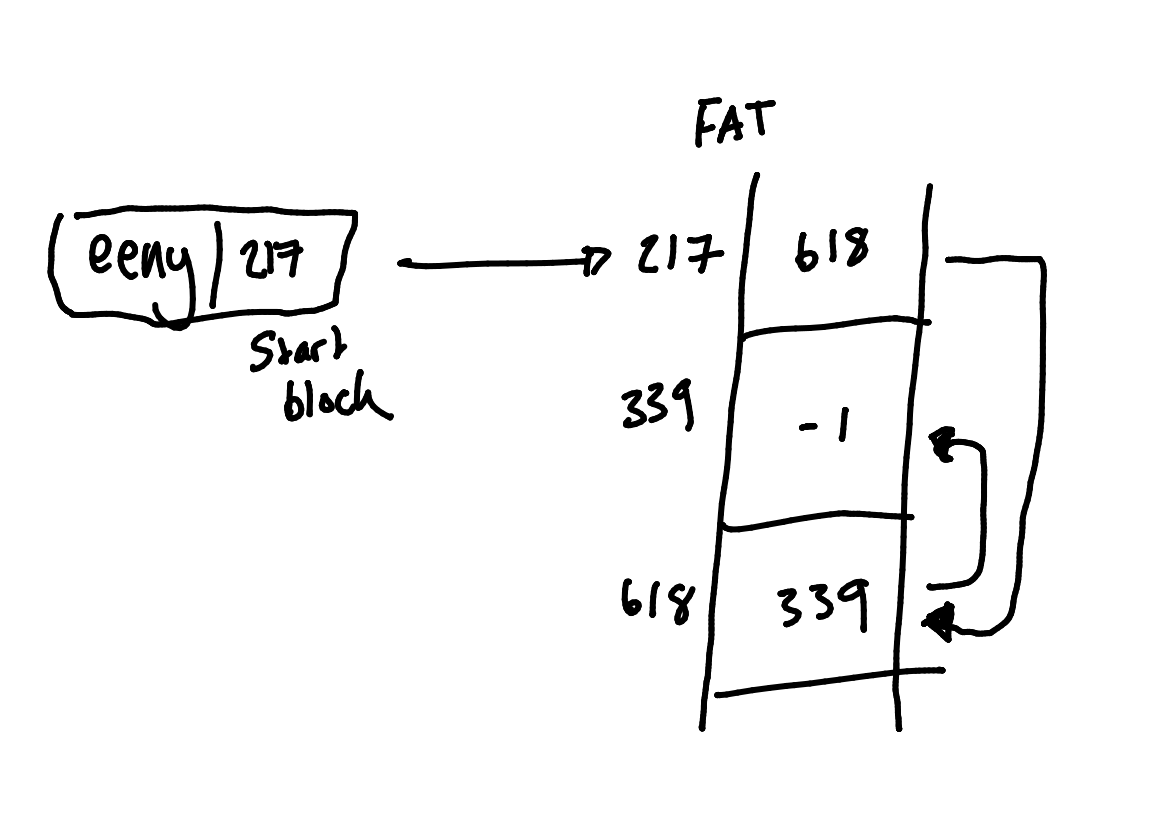
-1 is the end of the list of blocks.
0 indicates an unused block.
Advantages
- All pointer info held in one place (separate from the data).
- Easier to protect.
- No need for separate free list.
- Direct access much more efficient.
Problems
- May require drive head to shift constantly between the FAT and file blocks.
- FAT may become huge for large disks.
Indexed Allocation
First block holds index to all other blocks in the file.
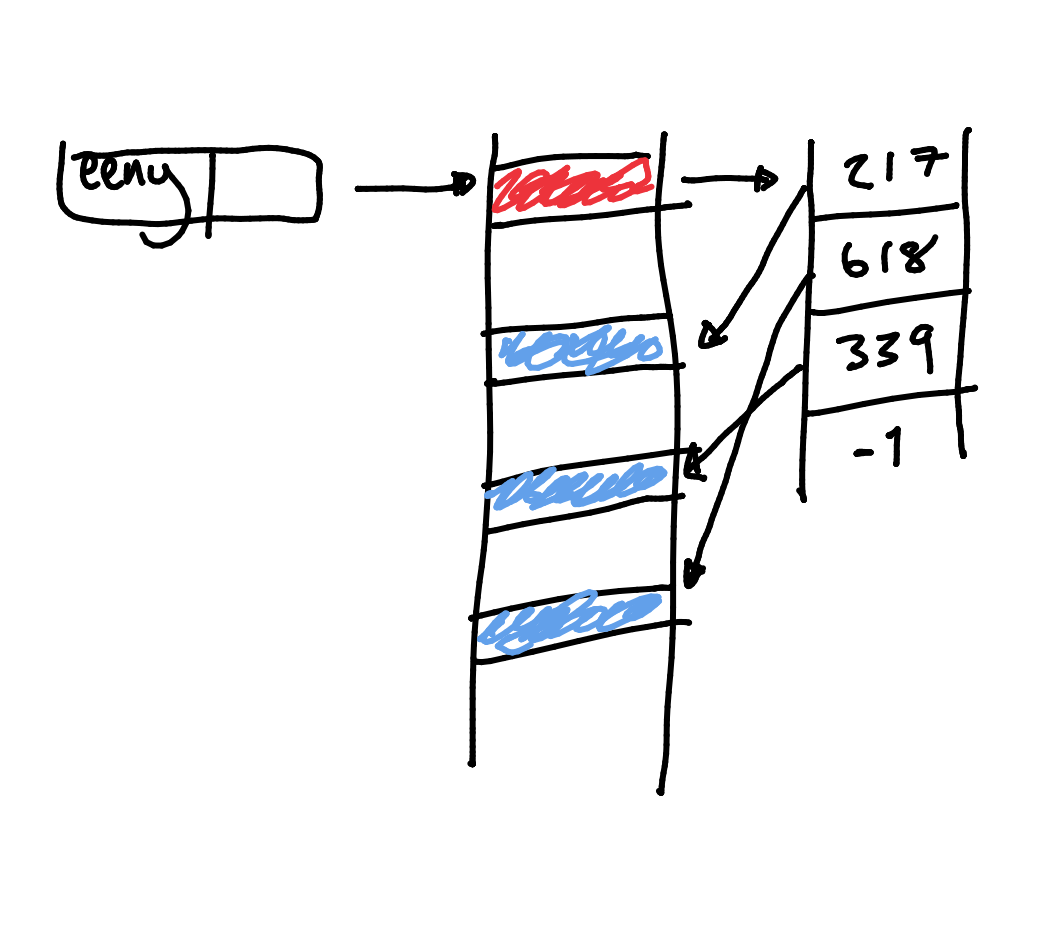
The inode is what points to the first block in a file.
Advantages
- Each file’s pointer info is held in one place.
- Very efficient for both sequential and direct access.
Problems
- Blocks may still be widely dispersed.
- Can tun out of pointers for large files.
- May have to chain several index blocks together.
Example - NTFS
- Has a master file table (MFT) using a form of indexed allocation.
- Files under 1 block will be contained entirely within the MFT to save space.